출처: 네이버 부스트코스 인공지능(AI) 기초 다지기 3. 기초 수학 첫걸음
<목차>
1. numpy
- ndarray
- dtype, nbyte
- shape
- ndim, size
2. Handling shape
- reshape
- flatten
3. Indexing
4. Slicing
- numpy
- 파이썬 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지
- Matrix와 Vector 같은 Array 연산의 사실상 표준
- 장점: 일반 List에 비해 빠르고, 메모리 효율적 / 반복문 없이 데이터 배열에 대한 처리를 지원함
- 단점: C로 구현되어 있어 성능을 확보하는 대신 python의 가장 큰 특징은 dynamic typing을 포기함
- numpy performance
- 일반적인 속도 순 : for loop < list comprehension < numpy
- concatenate 처럼 계산이 아닌, 할당에서는 연산 속도의 이점 없음
- ndarray (numpy dimension array)
- numpy의 기본이 되는 단위
- 일반적인 numpy 호출 방법
import numpy as np- np.array(data ,datatype) 함수를 활용해 배열 생성 -> ndarray
- numpy는 하나의 데이터 type만 배열에 넣을 수 있음
test_array = np.array([1,2,3], float) #지정한 data type에 따라 메모리 공간 크기가 달라짐
print(test_array) #array([1., 2., 3.])
type(test_array[2]) #numpy.float64 //64bit
test_array2 = np.array([1,2,3], int)
type(test_array2[2]) #numpy.int32- List와 가장 큰 차이점은 Dynamic typing은 지원하지 않는다는 점임 (C의 Array를 사용해 배열을 생성함)

a= [1,2,3]
b=a
a[0]=4
print(a) #[4,2,3]
print(b) #[4,2,3]a= [1,2,3]
b=a[:]
a[0]=4
print(a) #[4,2,3]
print(b) #[1,2,3] 바뀌지 않는다import copy
a = [1,2,3],[4,5,6]
b = copy.deepcopy(a)
b[0][0] = 7
print(a) #([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
print(b) #([7, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])

test_array = np.array([1, 4, 5, "8"], float)
print(test_array) #[1. 4. 5. 8.]
print(type(test_array[3])) #<class 'numpy.float64'>
# String Type의 데이터를 입력해도 자동 형변환을 실시
print(test_array.dtype) #float64
print(test_array.shape) #(4,)- dtype : numpy array의 data type을 반환함
- shape : numpy array의 object dimension 구성을 반환함
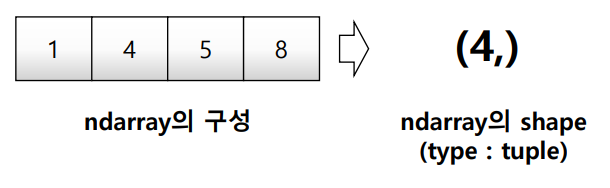
Shape
matrix = [[1,2,5,8], [1,2,5,8], [1,2,5,8]]
np.array(matrix, int).shape #(3,4)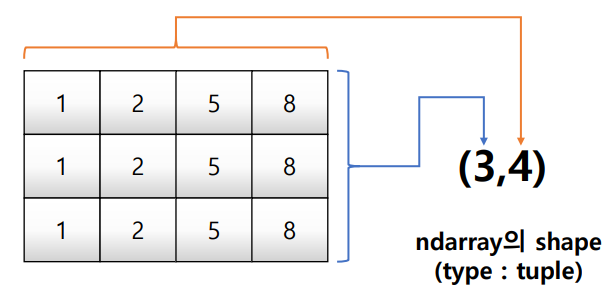
tensor = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]]
np.array(tensor, int).shape #(4,3,4)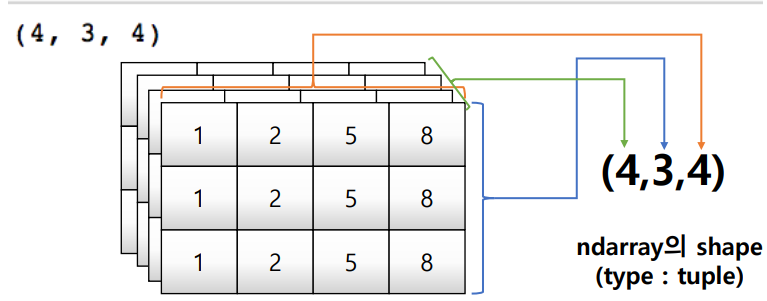
Array Shape - ndim & size
- ndim : number of dimension (몇 차원이냐)
- size : data의 개수
matrix = [[1,2,5,8], [1,2,5,8], [1,2,5,8]]
np.array(matrix, int).ndim #2
np.array(matrix, int).size #12tensor = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]]
np.array(tensor, int).ndim #3
np.array(tensor, int).size #48
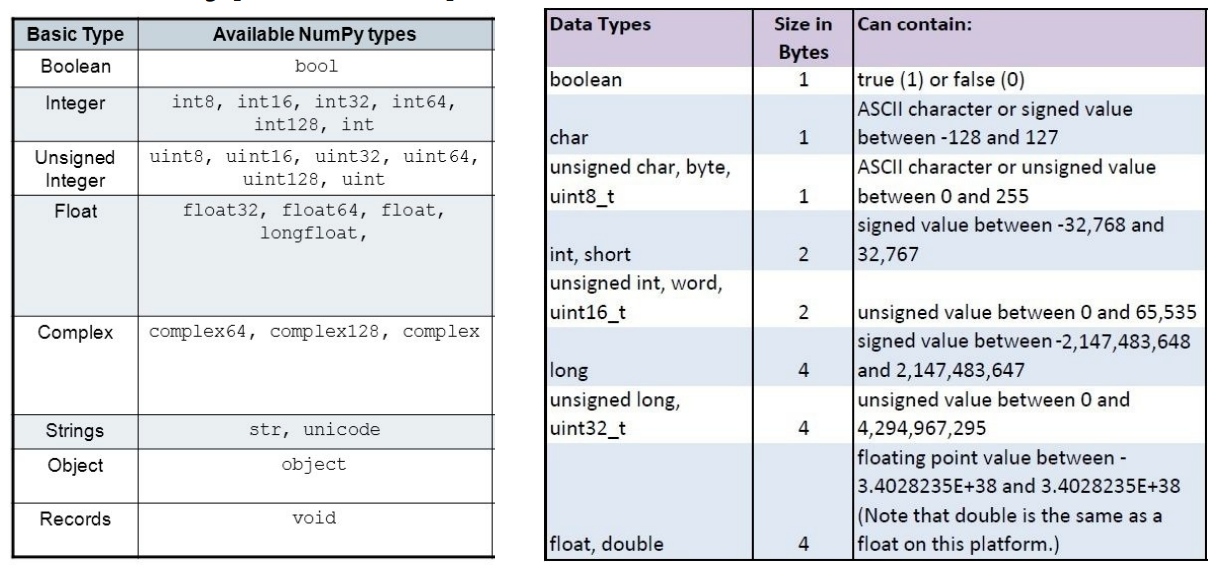
Array dtype
- 각 element가 차지하는 memory의 크기가 결정됨
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4.5, 5, 6]], dtype=int)
a.dtype #dtype('int32')
b = np.array([1,2,3], np.float32)
b.dtype #dtype('float32')Array nbyte
np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4.5, "5", "6"]],
dtype=np.float32).nbytes #24 = 4byte(32bit)*6
np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4.5, "5", "6"]],
dtype=np.int8).nbytes #6 = 1byte*6
- C의 data type과 compatible
- Handling shape
Reshape
- Array의 shape의 크기를 변경함 (element 갯수는 동일)
- y 값이 주로 vector 형태로 뽑아지는데, sklearn 모듈에서는 벡터형태가 아닌 "matrix" 형태로 들어가야해서 reshape를 사용해 변환시킴
test_matrix = [[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]]
np.array(test_matrix).shape #(2, 4)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(2,2,2)
'''
array([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[1, 2],
[5, 8]]])
'''
test =np.array(test_matrix).reshape(8,)
test #array([1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8])- -1의 뜻은 size를 기반으로 row의 개수 선정 (two-dimensional로 만들어 줄 수 있음)
test.reshape(-1, 1)
'''
array([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[1],
[2],
[5],
[8]])
'''
Flatten
- Array의 shape의 크기를 변경함 (element 갯수는 동일)
- 딥러닝 초기모델을 배울 때 보통 nlist를 사용함(문자를 벡터 형태로 표현한 것). 기본적으로 28 x 28의 numpy array로 되어있음
test_matrix = [[[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]]]
np.array(test_matrix).flatten()
#array([1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8])- Indexing
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4.5, 5, 6]], int)
print(a)
print(a[0,0]) # Two dimensional array representation #1
print(a[0][0]) # Two dimensional array representation #2
a[0,0] = 12 # Matrix 0,0 에 12 할당
print(a)
a[0][0] = 5 # Matrix 0,0 에 5 할당
print(a)
'''
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
1
1
[[12 2 3]
[ 4 5 6]]
[[5 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
'''- Slicing
- List와 달리 행과 열 부분 나눠서 slicing 가능
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]], int)
print(a[:,2:]) # 전체 Row의 2열 이상
'''
[[ 3 4 5]
[ 8 9 10]]
'''
print(a[1,1:3]) # [7 8] 1 Row의 1열 ~ 2열
print(a[1:3]) # [[ 6 7 8 9 10]] 1 Row ~ 2Row의 전체
'전공공부 > 인공지능' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Numpy 3편 (0) | 2022.07.19 |
|---|---|
| Numpy 2편 (0) | 2022.07.19 |
| [코세라] Fundamentals of CNNs and RNNs (RNN) (0) | 2021.08.05 |
| [코세라] Fundamentals of CNNs and RNNs (CNN) (0) | 2021.08.05 |
| [모두의 딥러닝] 10강~12강 정리 (0) | 2021.08.04 |